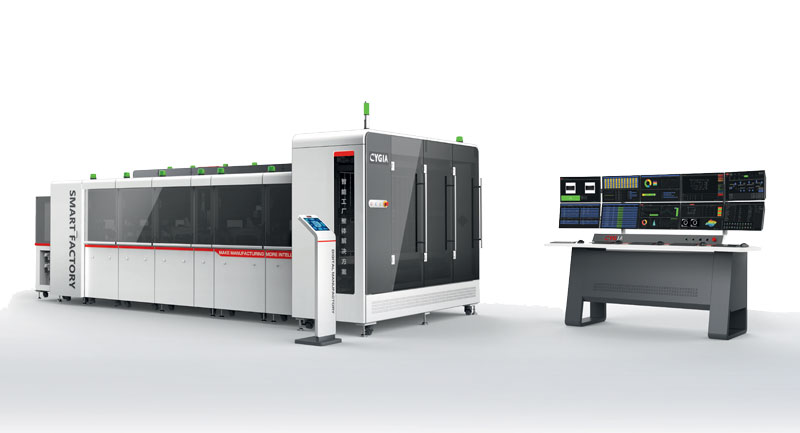
Electronics: the Smart Factory has PC-based Control
To develop a smart factory platform in electronics sector, two companies in China chose the PC-based control technology from Beckhoff: there are many benefits, first of all the integration in the Industry 4.0 perspective
Two Chinese companies, CYGIA (CYG Intelligent Automation) and CYGDM, have used PC-based control technology from Beckhoff. The first one is a high-tech company, and its business is customer-specific automation and test solutions for industries such as consumer electronics, semiconductors, automotive and medical engineering among others. CYGDM is a software and hardware services vendor specialized in developing and implementing smart factory solutions. Their aim was to develop a smart factory platform with unified interfaces and protocols as part of a new and flexible manufacturing strategy for electronics products. The platform combines sensors, actuators, operator terminals, control systems and communications equipment in an intelligent network that connects multiple users, including humans with machines, and machines with services. From an Industry 4.0 perspective, the platform maximizes integration, both at the device level and at the vertical and horizontal production levels.
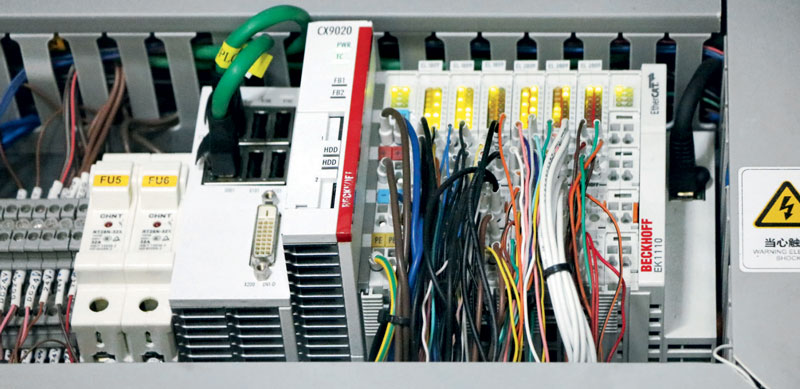
An open control technology
CYGIA’s smart factory solution utilizes IoT and monitoring technology to facilitate information management, to track the production process better, to reduce manual intervention on production lines, and to streamline production planning. Other technologies deployed as part of the solution include simulation, multimedia, and augmented reality. CYGIA and CYGDM chose powerful CX2030 and CX9020 Embedded PCs from Beckhoff to deliver the requisite computing power. The CX2030 handles higher-level hub control in the smart factory, while the CX9020 is used as control platform for distributed sub-stations. The open architecture of PC-based control, combined with ultra-fast EtherCAT communication technology, meets all their requirements when it comes to keeping response times as short as possible, while at the same time supporting time-division multiplexing and multitasking, programming in high-level languages, and extensive data storage capacity.
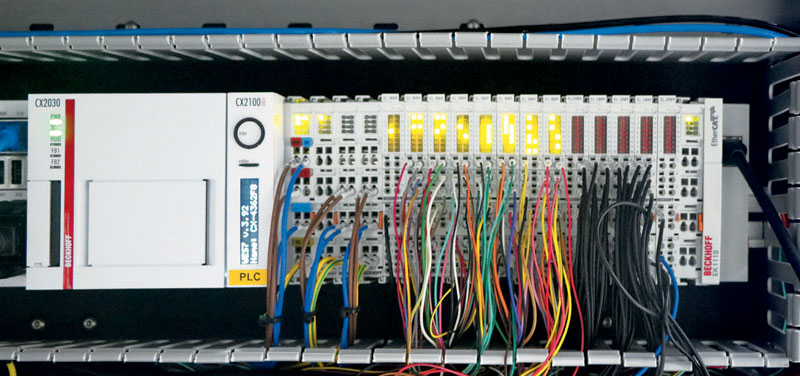
The benefits on the software side
The integration of the Beckhoff TwinCAT 3 automation software into Visual Studio® is a key benefit for CYGIA’s experts. In their view, the standardized bottom-layer control platform combined with the upper-layer control platform developed in .NET, has made it easier to integrate a wide variety of devices and to shorten the time required to develop their smart factory solution. Plus, being able to develop the software on a modular and distributed basis results in greater software efficiency. In the higher-level control system, they use both ADS.Net components and the Dynamic Link Library (DLL) to implement asynchronous communication between the server and multiple clients. The entire communication architecture, they claim, not only saves time, it is efficient and compatible too. In addition, the TwinCAT Automation Interface enables developers to program device interaction using COM technology. With TwinCAT, CYGIA’s engineers can use a unified, object-oriented, modular program framework, Structured Text, object-oriented programming and customer-specific libraries – all of which help streamline the development of this complex system.

Smart solution for mobile phone production
The software and hardware from Beckhoff fulfill CYGIA’s requirements for smart solutions in electronics manufacturing. Compared to a conventional setup with separate production stations, CYGIA’s system can achieve greater manufacturing and supply-chain flexibility and improve capacity utilization. For instance, it enables the ERP, MES and monitoring systems involved in the manufacture of mobile-phone circuit boards to exchange data, resulting in comprehensive process automation that spans everything from order handling to transportation. The main elements in the automated production line include hollow-board printing, surface mounting, reflow welding, dispensing, screw locking, automated optical inspection, integrated and functional circuit testing, and packing and unpacking. The line has three CX2030 Embedded PCs, which communicate at extremely high speed with the higher-level central control system. The master CX2030 runs both the PLC program and the motion control and HMI software. The second CX2030 Embedded PC runs PLCs, motion control and HMI software, handles communication over TCP/IP, and exchanges data with the ALC line control system. The third CX2030 handles PLCs, motion control and HMI software, and in addition controls a high-resolution TCP/IP camera for optical inspection.
The choice of EtherCAT technology
CYGIA chose EtherCAT as a high-speed communication system to ensure fast, precise transmission of sensor signals. The company runs master communication on its automated production line over EtherCAT in a star topology. Slave devices are easy to connect, which simplifies management, maintenance and expansion. A line topology is used at sub-station level to keep the wiring as simple as possible.
The main goals for the future
CYGIA’s aim with its smart factory solution is to integrate assembly and manufacturing units for discrete electronic components within a unified production system. Other goals are to connect production plants, to visualize production data, to make production processes transparent, and to create fully automated production sites. Given the broader trend toward Industry 4.0, CYGIA also needed smart factory software that would enable access to a wide range of data resources, including cloud computing, big data, and IoT. With TwinCAT 3, the company has found the right solution and is now looking forward to the new production model that has lined up. They will gradually incorporate TwinCAT 3 functionality to support big data analysis, IoT advancements, and machine vision in future upgrades. This will further enhance the setup of the hybrid control system to fully exploit the benefits of cloud data storage and distributed data interaction.

