German Machine Tool Industry Sees a Glimmer of Light
The VDW (German Machine Tool Builders’ Association) expects production in the German machine tool industry to grow by 6 per cent to around 12.6 billion euros in 2021. At the association’s annual press conference, Chairman Dr Heinz-Jürgen Prokop stated that the improved mood in the economy is raising the willingness to invest.
“After two years of great restraint, there is now a strong need to make up ground,” These are Dr Heinz-Jürgen Prokop’s comments about 2021 trends of the German Machine Tools market”. The global Purchasing Managers’ Index and the German ifo Business Climate for the capital goods industry are on course for growth. China is now the principal driving force behind the global economy. The USA, too, is providing a boost following US President Biden’s election victory. “However, the prerequisites for companies’ regaining their confidence and investing are beating the corona pandemic and sketching out a sensible roadmap for gradually emerging from lockdown,” said Prokop.
The automotive industry in particular, the largest customer for machine tools, is benefiting from the upswing in China. Electronics, food processing, logistics and parts of the medical technology sector having been doing good business anyway during the crisis. This is set to continue. In Europe, too, investments are expected to rise again by 10 per cent after the major slump. The last two years have been very difficult for many reasons, but this restraint is now having a positive effect on the machine tool industry. Oxford Economics, the VDW’s forecasting partner, is predicting strong growth of 35 per cent for orders in 2021. There were already indications of this in November and December. “Nevertheless, it won’t be easy to get back to pre-corona levels,” explained Heinz-Jürgen Prokop.

2020: a turbulent year for production, exports and domestic sales
Orders fell by 30 per cent in 2020 due to the corona crisis, following a decline of a similar magnitude the year before. All other key figures also slipped deep into negative territory in 2020: production was down 31 per cent, exports down 29 per cent, domestic sales down 33 per cent. The hoped-for turnaround in the current year is thus starting from a low level.
In 2019, capacity utilisation was still at 88 per cent. The decline in orders caused this to fall to just under 72 per cent in 2020. This is comparable to the levels seen following the 2009 financial crisis. The annual average of employee numbers fell by 4.5 per cent to 70,000 men and women in 2020. “Nevertheless, given the sharp decline in production, it’s obvious that companies are trying to keep their highly skilled employees for as long as possible. The instrument of short-time work remains useful and necessary here,” said Prokop.
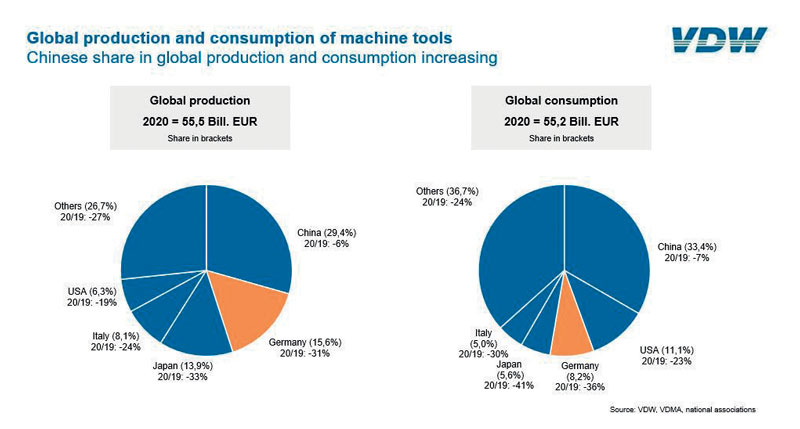
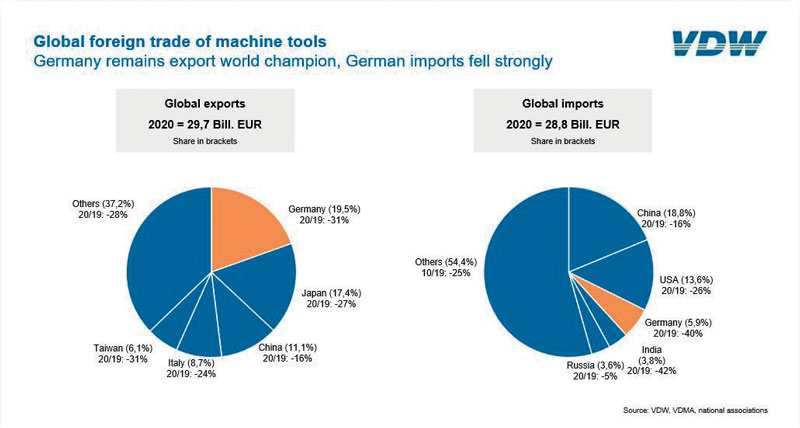
Solid international performance despite the high losses
Despite the high losses, German manufacturers have performed well when compared internationally. The German industry accounts for a 16 per cent share of international production, ranking behind China but ahead of Japan. It also remains the world export champion, taking a 20 per cent share, ahead of Japan and China.
Machine tool sector demanding technology offensive for environment-friendly mobility
The German machine tool industry sees attractive opportunities in the Green Deal and the 2050 climate protection targets. With its Euro 7 standard, the EU Commission is now planning to set the emissions limit for cars and trucks to zero by 2025.
The VDW supports the conclusions of a recently published VDMA position paper (VDMA is the largest network organization for the mechanical engineering industry in Germany, editor’s note). It calls for a technology offensive in favour of environmentally friendly mobility. The aim is for the organisations to work together with industry to achieve climate neutrality, and to draw upon the strengths of companies in developing new technologies. For this reason, many different technologies should be deployed to reduce exhaust gas and CO2 emissions. In the future, this will include the use of hydrogen and synthetic fuels in vehicles, and also further optimisation of the combustion engine, the use of fuel cell technology and a growing number of battery-powered vehicles. “Relying solely on electromobility would lead to an extreme increase in electricity demand, which could not currently be covered by renewable energy,” said Prokop. “The EU is called upon to launch a broad-based modernisation campaign and to provide the required framework,” he concluded. In addition to the automotive industry, this would also support the transformation process in user industries such as the construction sector and agricultural machinery manufacturers.

